
No room! No room!they cried out when they saw Alice coming.
The exclusion problem is to remove as few cells as possible from a given region of the grid so as to exclude a given polyform. Equalization problems involve equalizing the distribution of cells within a region. The variegation problem is to color the cells of the grid with as few colors as possible so that a given polyform, no matter where it lies on the grid, has cells of all different colors. Integration means joining copies of a weakly joined polyform to make a strongly joined polyform.
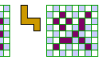 | Hexomino Exclusion. Exclude a hexomino from a checkerboard. |
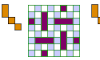 | Polyking Exclusion. Exclude a polyking from a checkerboard. |
 | Polyiamond Exclusion. Exclude a polyiamond from the plane. |
 | Polyhex Exclusion. Exclude a polyhex from the plane. |
 | Polycairo Exclusion. Exclude a polycairo from the plane. |
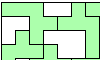 | Connected Polyomino Magic Squares. Arrange adjacent copies of a pentomino in a square grid to place the same number of cells in each row and column. |
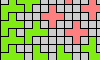 | Two-Pentomino Magic Squares. Arrange copies of two pentominoes in a square grid to place the same number of cells in each row and column. |
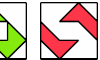 | Polyabolo Magic Squares. Arrange copies of a polyabolo in a square grid to place the same number of cells in each row and column. |
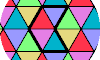 | Polyiamond Variegation. Color the cells of the polyiamond plane so no copy of a polyiamond has duplicate colors. |
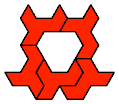
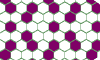
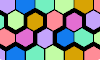 | Polyhex Variegation. Color the cells of the polyhex plane so no copy of a polyhex has duplicate colors. |
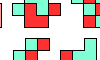 | Polyking Integration. Join copies of a polyking to form a polyomino. |
 | Polyming Integration. Join copies of a polyming to form a polyiamond. |
 | Didrifter Integration. Join copies of a didrifter to form a polydrafter. |